The earth is the planet where we live. We live have in different regions with distinctive natural environments. Naturally, our lifestyles, societies, cultural, economic and political activities have unique characteristics. All these things are the topic of discussion in modern geography. So, geography is a science of nature and it is a science of environment and society. In this article we are going to deal with geography and environment, their scope, different branches of geography and the importance of geography as a subject.
At the end of this article, we will be
able to:
• Explain the idea of geography and environment.
• Describe the scope of geography.
• Explain the importance of studying geography and environment.
• Explain the inter-relationship among different elements of
geography and environment.
Concept of Geography
The word geography is derived from two Greek words 'geo' (earth)
and 'graphy' (description). But the discipline does not simply describe the
earth, it explores the planet as peoples, habitat. Eratosthenes was the first
Greek scholar who used the term 'geography' as the study of earth as human
habitat. Professor E.A Macnee said, 'geography is the study of environment of
man both physical and social, particularly in its relation to human activites.'
Professor L. Dudley Stamp has defined geography as, 'A description of the world
and of its inhabitants.' Professor Carl Ritter said, that geography is
concerned with the objects on the earth's surface around man. Geography is the
science of nature, environment and social science. According to Richard Hartshorne,
'geography provides accurate, orderly and rational description and interpretation
of the variable character of the earth's surface.'
Academy of Science of Washington D.C. gave a definition of
Geography in 1965. According to them, Geography searches for how the
sub-management of natural environment of the surface and how human beings
adjust themselves with these natural phenomena or physical body.
People live in this world and lead their life on it. The natural
environment influences their way of living. Climate, physical features, natural
vegetation, animals, rivers, seas, and mineral resources which influence the
life of the people in different ways. Activities of man change the environment,
such as, their homes, roads, ports and cities change the nature and environment
in different ways. Settlement is built by cutting trees, by filling up canals,
wetlands, and ponds. There is interaction between man and environment.
The main function of geography is to find out the cause of
interaction between man and environment.
Concept of Environment
People live in an environment. An environment is made up of rivers,
oceans, mountains, forests, settlements, roads, plants, animals, water, soil
and air. All activities of human beings have profound effect on natural and
man-made features of the environment. Environmental scientist Arms said,
'environment is the surrounding organic and natural situations of animals.'
C.C. Park says, environment means the sum of all the situations
of humans at certain point of place and time.
Environment changes with the change of time and place. For
example, at the beginning of mankind, water, air, plants and animals made up
the environment. Later, human interference, social, economic, cultural and
political activities developed a new environment i.e. human environment.
Elements of environment
Environment is made of two kinds of elements – living and non
living elements.
Those who have life, take food, have intelligence, have birth/death
and growth are living things/elements. Trees, birds and animals, insects, humans
and other animals are living things. These are the living elements of environment.
Earth, water, air, mountains, rivers, seas, light, temperature, moisture are
the non living things/elements. They make non living environment.
Task : Make inter-relationship among different elements of environment.
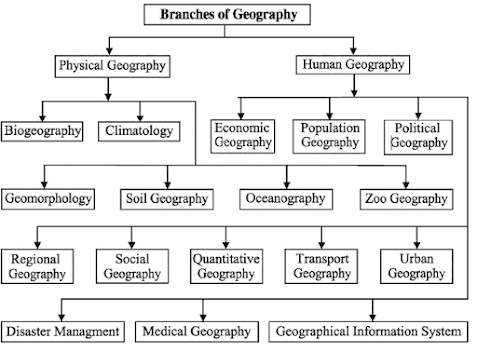
Scope of Geography
Science and technological expansion, new inventions,
innovations, expressions of thoughts, change of social values have extended the
scope of geography. So, various subjects such as Geomorphology, Climatology,
Oceanography, Soil Science, Botany, Sociology, Economics, Politics and History
etc. have been included in Geography.
Branches of
Geography
(a) Physical Geography : Physical Geography is that
branch of Gerography dealing with the natural features of the earth, the home
of human beings. Physical Geography deals with water, air, animals, and the
land of the planet earth i.e. everything that is part of the four spheres-the
atmosphere, biosphere, hydrosphere and lithosphere.
1. Geomorphology : Geomorphologists study the
landforms of the planet, from their development to their disappearance through
erosion and other processes.
2. Climatology : Climate geographers
investigate the distribution of long term weather patterns and activities of
the earth's atmosphere.
3. Biogeography : Biogeography studies the
distribution of plants and animals on or near the surface of the earth.
4. Soil geography : Soil geographers study the
upper layer of the lithosphere, the soil of the earth and its categorization
and patterns of distribution.
5. Oceanography : Oceanography discusses the
transport and communication among continents through ocean, the rise and fall
of ocean surface and the management of ocean resources.
(b) Human Geography: Human geography is a major
branch of geography that studies people and their interaction with the earth
and with their organization of space on the earth's surface.
1. Economic Geography : Economic geography
examines the distribution of production of goods, the distribution of wealth
and the spatial structure of economic condition.
2. Population Geography : Population geographers are
concerned with the distributions, migrations and growth of population in
geographic areas.
3. Regional Geography : Regional geographers focus
on areas as large as continents or as small as an urban area.
4. Political Geography: Political geography
investigates all aspects of boundaries, country, state and national
development, international organizations, diplomacy, internal country sub
divisions, voting and more.
5. Quantitative Geography : Quantitative
Geography uses quantitative techniques and models to test hypothesis.
Quantitative methods are often used in many other branches of Gerography but
some geographers specialize in quantitative methods only.
6. Transport Geography : Transport geographers
study both public and private transport networks and the use of those networks
for transporting people and goods.
7. Urban Geography : Urban Geography deals with
the orgm, evolution, classifications, environment, and different areas of cities
and towns.
8. Disaster management : Disaster management
focuses on how to reduce loss during disaster and how to protect environment
and ocean from disaster.
Whatever branch we discuses, environment is always an issue. At
present Geography and Environment are taught in integrated way. Natural and
social environment bear equal importance in geographical science.
Types of environment
There are two types of environment--natural environment and social
environment.
Earth, water, air, mountains, rivers, seas, light, trees, birds,
animals and insects, constitute natural environment. On the other hand human
behaviors, rituals, education, values, economics and politics constitute social
environment.
Importance of Studying Geography and Environment
The disciplines deal with:
• The environment of the
world, the nature of a particular place, the origin and structure of particular
landforms i.e. hills, mountains, river, sea, plains and deserts.
• Origin
and evolution of the earth along with the evolution of plants and animals.
• Plants and animals of
different environments--their behaviors, food habits, and their habitats.
• How social environment
has changed due to the development of agriculture, industry, trade and
commerce, transport and communication.
• How natural calamities
occur, how to control them and what harm they do to the human beings.
•
How human interference spoils the environment-- the intensity of the damage, the
cause of the rise of temperature and the greenhouse effect as well as their influence
on the environment and how to minimize the loss.
• How to develop human resources for economic development by
utilizing natural resources.
• Ocean and the management of its resources.