The diversified outward appearance of the earth is known as the external structure of the earth. Some principal and important examples are described below.
Main Landforms of the Earth
Earth's topography is made up of many different types of
landforms. While the planet is covered primarily with water, the three major
types of landforms are mountains, plains and plateaus. These can be formed by a
variety of natural forces, including erosion from water and wind, plate
movement, folding and faulting, and volcanic activity.
Mountains
While most mountains are created due to the slow and gigantic
movement of the earth's tectonic plates, some are formed as a result of erosion
and volcanic activities. Mountains are characterized by a higher elevation as
compared to the surrounding areas. They are higher than 600 metres, and taller
and steeper than the hills. The world's tallest mountains The Himalayas are
located in Asia and the largest range of mountains is present in the Atlantic
ocean. You will be surprised to know that some of the highest mountain peaks
are located deep in the oceans. There are some mountain which is not a part of
a mountain range but exists in isolation such as Mount Kilimanjaro in East
Africa.
Mountains : Types and their Formation
An elevated landform is identified as a mountain if it has a
summit and there are slopes on its sides. They are basically made up of earth
and rock materials. Regarding mountain formation, the outermost layer of the
earth or the earth's crust is composed of six tectonic plates. When two plates
move or collide with each other, vast land areas are uplifted, resulting in the
formation of mountains. Depending upon the geological processes responsible for
uplift of mountains and landform characteristics. There are four major types of
mountains.
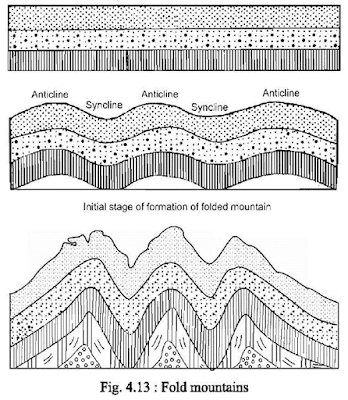
Fold mountains : Fold
mountains are the most common type of mountains. They
are formed due to collision of two plates, causing fold that descends on both folding
of the earth's crust. The sides is called Anticline, whereas, the fold that ascends
from a common low point (on both sides) is called Syncline (fig. 4.13). Examples
of fold mountains are the Himalayas located in Asia, Rocky mountains located in
North America, and the Alps located in Europe.
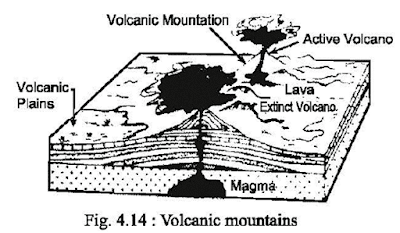
Volcanic mountains : Volcanic
mountains are created due to volcanic eruptions. When this lava erupts and
piles up on the surface of the earth, it cools and solidifies to form a
volcanic mountain. In many instances, the volcanic materials erupt to great
heights due to pressure from under the earth’s crust (fig. 4.14).
Examples of volcanic mountains are the Mount Fujiyama in Japan, Mount
Vesuvius in Italy and Mount Pinatubo in Philippines.
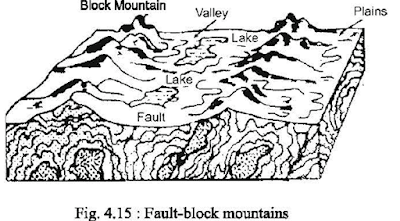
Fault-block mountains: Due to tectonic movement in
the earth's surface contraction and expansion of rocks takes place. This
movement creates cracks in the earth's surface which leads to displacement of
the earth’s surface. It is called Fault.
Fault mountains or fault-block mountains are created when blocks
of rock materials slide along faults in the earth's crust.
There are two types of block mountains, viz.,
the lifted and tilted. In the former type, the mountain has two steep sides, whereas, the
tilted type has one steep side and a gentle sloping side (fig. 4.15). Examples
of fault-block mountains are the Vindhya mountains and Satpuras mountain in
India, Salt mountain in Pakistan and Black forest of Germany.
Dome/Laccolith mountains : Dome
mountains are built when the hot magma rises from the mantle and uplifts the
overlying sedimentary layer of the earth's crust. In the
process, the magma is not actually erupted, but it cools down and hardens,
thereby forming the core of the mountain. As their appearance resembles a dome
shape, they are called Dome Mountains or Laccolith Mountains (fig. 4.16).
These do not have any summit. Example of dome mountain is the
Henry mountain in USA.
Plateaus
Plateaus are formed by various geologic activities, such as immense lava flows, uplifting due to tectonic plate collisions, and sediment plateaus formed from eroded material from mountains. Plateaus are lower than mountains but higher than plains with steep slopes and extensive undulating surface is known as plateau (fig. 4.17). The height of the plateau varies from few hundred metres to few thousand metres. The height of the highest plateaus of the world varies from 4270-5190 metres.
On the basis of the location, plateaus can be classified into
three categories :
1. Intermontane plateau
2. Piedmont plateau
3. Continental plateau
1. Intermontane plateau : This type
of plateau is surrounded by mountains. The Tibetan
plateau is an intermontane plateau where The Kunlun mountain is in the
north, The Himalayas in the south and it the east and west there are mountains,
Bolivia in South America, Mexico in Latin America, and Mongolia
and Tarim in Asia is this type of plateau (fig. 4.18).
l. Piedmont plateau : When high mountains are
eroded and the sediments are deposited at the foothills and creates plateau is
known as piedmont plateau. Colorado in North America and Patagonia in South
America are the piedmont plateaus.
3. Continental plateau : Extensive highland
surrounded by sea and lowlands is called Continental Plateau. These type of
plateaus have no link with the mountain. Examples are Spain, Australia, Saudi Arabia,
Greenland and India.
Plains
Extended lands with gentle slope a bit high from the sea level
is called plain land. The plains are formed by the erosional and depositional
work of different land forming agents like river, glacier and wind. Gently
sloping and undulating land is suitable for agriculture, settlement and road
construction. On the basis of origin the plains are classified into two
categories : Erosional and depositional plains.
Erosional plains : This type of plains are
formed for erosion by river, wind and glacier. The upper rocks are eroded
gradually and the lands with steep slope are transformed into plains. The
plains at the foothills of Appalachian mountains and the plains of Finland and
Siberia are these type of plains. The Barind and the Madhupur Tract of
Bangladesh are examples of erosional plains.
Depositional plains: Natural processes of river,
wind and glacier transport the sand dust and sediment, from one place and
deposit in a lowland forming a depositional plain. Formation of depositional
plains are found from the mountainous region to the sea coast. River can form
valley such as the valley of Nepal. It can form alluvial fan at the foothills
of the mountains by deposition. In the middle course of a river, where velocity
of the river is reduceds it overflows the banks causing flood during rainy season
and the sediments are deposited gradually on both sides of the river forming a
plain land which is known as flood plain. Flood plains of Dhaleswari and Jamuna
are of these type. A plain land formed at the mouth of the river
through deposition is known as Delta. Ganges delta is located in the southern
part of Bangladesh.
Plains are also formed in the coastal areas by the activity of ocean current. These are known as coastal plains. Coastal plain of Bangladesh stretches from Feni river to Teknaf. Plains are also formed by the deposition of glacial moraines in the cold regions of the world. The Prairie of Canada are formed from the glacial deposits.
Learn more about -