Removing waste is a problem, and it can also present an entrepreneurial opportunity. We will try to examine ways in which waste products that we usually pay to have hauled away can now generate revenue. Whether its’s recycling aluminum cans or cardboard, or garbage that could be used to feed animals, our aim of this article is to come up with solutions to this entrepreneurial-oriented problem.
In this article we will -
• Try following the step of the creative problem-solving process and clearly identify the problem• Next, gather data and formulate the challenge.
• Then, explore ideas and come up with solutions.
• Develop a plan of action.
• Finally, note how we would evaluate the effectiveness of our solution.
1. Identify the problem
Removing waste that could damage our ecosystem.
2. Gather data and formulate the challenge
· How to remove waste
· How to make waste problem become a profit
· How to manage and reduce waste
3. Solutions to the problem
Source Reduction and Reuse - Reducing waste at the source is achieved by expanding recycling efforts through creating recycling networks and providing on-site food waste treatment facilities at residential and commercial properties. The objective is to reduce the heavy reliance on raw materials that are continuously getting depleted, in an effort to conserve the environment.
Landfills - It involves burying trash in the land while taking measures to eliminate both odors and the risk of toxic substances seeping into the ground and contaminating water sources.
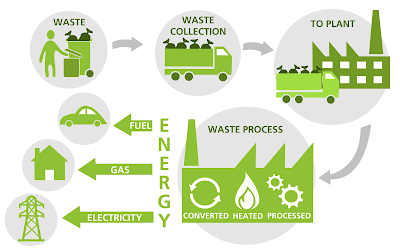
Combustion/Incineration - Also referred to as thermal treatment, this method can also be used to generate heat, gas, and steam for power.
Composting - This is a natural bio-degradation process of organic wastes (kitchen waste and plant remains) that converts them into nutrient-filled food for plants. This is a common technique in organic farming, where the organic materials sit in one place for months to allow for decomposition.
Recovery and Recycling - Recovery involves the use of discarded items for other meaningful uses. Recycling of scrap metal, paper, glass, plastics and cardboard, is a large industry in many developed countries, but use of recycled materials is often not well developed.
Aluminum Recycling – aluminum is the one of the easiest materials to recycle – they are melted at s high temperature and remolded into cans.
Computer Recycling - Computers are made from a large number of different plastics, metals and a great deal of other materials that can be recycled.
Glass Recycling - Glass is a relatively easy material to melt down and remake into many different kinds of shapes.
Mattress Recycling - Mattresses are usually made from a large number of materials, including metal, fabric and plastic. When sent to a recycling plant, they are separated from each other and recycled at a success rate of 95%.
Reselling Used Appliances - Just like computer recycling, reselling used appliances involves buying them off from people that no longer need them, sprucing them up and selling them for a profit.
Plastic Recycling - Plastic recycling is by far the most common kind of recycling today. Most types of plastic can be recycled rather than ending up in landfills and dumpsites, of which they are the largest constituent.
Paper Recycling - Most kinds of paper are relatively easy to recycle.
Tire Recycling - At such plants, they are melted and can be molded into new products. Most times, they are simply sold in blocks after going the recycling process to be used further.
Battery Recycling - Almost every kind of battery can be recycled through a process that involves sorting, sieving and creating new parts that can be used in batteries once again.
Food Waste Recycling - the most effective methods are home compositing and contacting local authorities when the food in question cannot be composted at home.
Textile Recycling - This can then be reused in the manufacture of new clothes or for reinforcing some types of furniture.
Recycling Junkyard Furniture - creating usable furniture from discarded pieces is a very profitable venture.
Reduce - organization should encourage employees to only print what they need and ensure that printer settings are defaulted to print double sided to save paper.
Reuse – For example, encouraging occupants to use reusable coffee mugs rather than single-use, disposable cups, you don’t have to manage the disposal of a bunch of coffee cups.
Donate - Organizations can donate products or materials to others who need and can use the items. For example, restaurants, hotels and cafeterias promptly distribute perishable and prepared foods to hungry people in their communities.
Developing a Plan of Action
· Buy in Bulk - refill containers and avoid single use products like creamers and sugars
· Rent or lease non-essential equipment
· Go paperless - use online resources and subscriptions instead of phone directories, newspapers and magazines and to share documents and presentations
· Use reusable cups, dishes, cutlery; install a dishwasher
· Install electric hand dryers or use washable linens
· Place clearly labeled recycling bins next to each garbage bin and at each work station
· Save single sided paper for scrap note paper and reuse envelopes
· Recycle cardboard and paper
· Have multi-stream recycling containers for plastics, plastic film, tin, glass, beverage containers
· Source separate construction waste - wood, concrete/asphalt, metal, etc
· Properly dispose of fluorescent bulbs, batteries, computer products
· Properly dispose of motor oil (containers, filters, oil), antifreeze, tires, corrosives, flammables and poisonous products
· Encourage litterless lunches
· Buy products with recycled content
· Identify external waste impact for materials taken offsite - try to buy only reusable, recyclable or biodegradable products
· Conduct an internal waste assessment to determine what waste streams could be eliminated or reduced through a change in operations or purchasing habits
· Buy only biodegradable, non-toxic products for soaps, cleaners, and hygiene products - buy in bulk and reuse containers
· Develop sustainable purchasing guidelines to make sure items you buy are built to last, repairable, recyclable, biodegradable and/or resalable and made of locally sourced materials if possible.
Evaluate Effectiveness of Solution
Recycling is an effective way to remove waste. It prevents the emissions of many greenhouse gases and water pollutants, and saves energy. Using recovered material generates less solid waste. Recycling helps to reduce the pollution caused by the extraction and processing of virgin materials.
As long as avoidance of waste and reuse is not completely achievable, thermal waste treatment with recovery of energy and secondary raw materials is a necessary waste management option. It was shown that methods for the evaluation of to what extent sustainability goals are achieved by a certain waste management option exist.
Proper waste management is important to avoid contamination, especially when the waste is hazardous. But more importantly, households and businesses should exercise waste minimization or waste avoidance, which involves recycling old items, repairing broken items, donating items no longer in use, avoiding the use of disposable items, etc., to reduce the amount of waste that will end up in landfills.