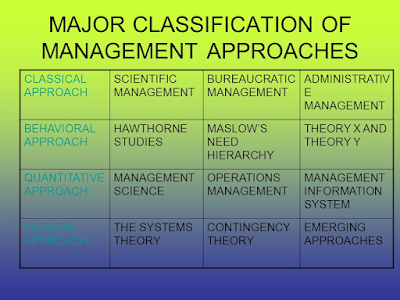
Classical model of management:
a.) Here productivity and efficiency are the most important things. It increases the work efficiency through mass production.
b.) Classical model of management is based on the belief that it is a mix of administrative, scientific and various other theories.
c.) It follows a structured approach with a hierarchy of management levels and the expectations that the employees have.
d.) Employees here are expected to perform tasks as per the procedures created ,in order to maximize the productivity.
Behavioral model of management:
a.) It focuses on the human relationships and their emotions. It mainly focuses on how a manager should treat his/her employees and how he should motivate them.
b.) It deals with how a individuals get motivated by social, psychological and economic factors. It determines a worker's attitude and their performance.
c.) Behavioral model relies on the following criteria-social status, relationships with co-workers, self fulfillment and empowerment.
d.) This is necessary to have a good and a friendly atmosphere while working in order to achieve job satisfaction.
Though classical model and behavioral model have their shortcomings, both are necessary to have a healthy working environment. And in a way, both the models are inter-dependent on each other. Both these models consist of certain rules and guidelines, which when followed, can help in establishing a successful organization. Everything here is interdependent and necessary to take any sot of decision regarding Information systems. Because, if the employees do not have cooperation and do not work well then there are chances that the organization can face losses and many other troubles. And also because no decision can be taken alone! Teamwork is necessary.
Quantitative Approach
It includes the application of statistics, optimization models, information models and computer simulations. More specifically, this approach focuses on achieving organizational effectiveness. Three main branches:
- Management Science
- Operations Management and
- Management Information Systems.
- Systems Theory
- Contingency Theory