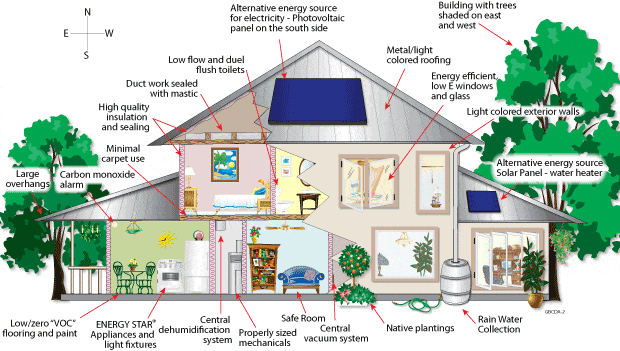
"A green building is one which uses less water, optimizes energy efficiency, conserves natural resources, generates less waste and provides healthier spaces for occupants, as compared to a conventional building."
Green construction or sustainable building refers to a structure and using process that is environmentally responsible and resource-efficient throughout a building's life-cycle: from siting to design, construction, operation, maintenance, renovation, and demolition.
${tocify}
Objectives
- Efficiently using energy, water, and other resources
- Protecting occupant health and improving employee productivity
- Reducing waste, pollution and environmental degradation
Buildings can be rated for their environmentally sustainable construction. One such rating system is the LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design). This building rating system was developed by the U.S. Green Building Council (GBC). The other rating systems are BREEAM (Building Research Establishment's Environmental Assessment method -United Kingdom)and CASBEE (Comprehensive Assessment System for Building Environmental Efficiency-Japan) help consumers determine a structure’s level of environmental performance.
What is LEED?
Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) is a rating system devised by the United States Green Building Council (USGBC) to evaluate the environmental performance of a building and encourage market transformation towards sustainable design.
The system is credit-based, allowing projects to earn points for environmentally friendly actions taken during construction and use of a building.
What types of buildings can use LEED?
LEED certification is available for all building types including new construction and major renovation; existing buildings; commercial interiors; core and shell; schools and homes. LEED systems for neighborhood development, retail and healthcare are currently pilot testing. To date, there is over 4.5 billion square feet of construction space involved with the LEED system.
How does LEED work?
LEED is a point based system where building projects earn LEED points for satisfying specific green building criteria. Within each of the seven LEED credit categories, projects must satisfy particular prerequisites and earn points.
The rating system addresses six major areas:
1. Sustainable sites;
2. Water efficiency;
3. Energy and atmosphere;
4. Materials and resources;
5. Indoor environmental quality; and 6. Innovation and design process.
LEED certification levels
four progressive levels according to the following scale:
- Certified 40–49 points
- Silver 50–59 points
- Gold 60–79 points
- Platinum 80 points and above
In 2004, the European Commission initiated the Green Building Program (GBP). This program aims at improving the energy efficiency and expanding the integration of renewable energies in non-residential buildings in Europe on a voluntary basis.
Green building materials offer specific benefits to the building owner and building occupants:
• Reduced maintenance/replacement costs over the life of the building.
• Energy conservation.
• Improved occupant health and productivity.
• Lower costs associated with changing space configurations.
• Greater design flexibility.
Green building material/product selection criteria
1. Resource efficiency
2. Indoor air quality
3. Energy efficiency
4. Water conservation
5. Affordability
1. Resource Efficiency
Resource Efficiency can be accomplished by utilizing materials that meet the following criteria:
• Recycled Content: Products with identifiable recycled content, including postindustrial content with a preference for postconsumer content.
• Natural, plentiful or renewable: Materials harvested from sustainably managed sources and preferably have an independent certification (e.g., certified wood) and are certified by an independent third party.
• Resource efficient manufacturing process: Products manufactured with resource efficient processes including reducing energy consumption, minimizing waste (recycled, recyclable and or source reduced product packaging), and reducing greenhouse gases.
• Locally available: Building materials, components, and systems found locally or regionally saving energy and resources in transportation to the project site.
• Reusable or recyclable: Select materials that can be easily dismantled and reused or recycled at the end of their useful life.
• Recycled or recyclable product packaging: Products enclosed in recycled content or recyclable packaging.
• Durable: Materials that are longer lasting or are comparable to conventional products with long life expectancies.
2. Indoor Air Quality (IAQ)
Indoor Air Quality (IAQ) is enhanced by utilizing materials that meet the following criteria:
• Low or non-toxic: Materials that emit few or no carcinogens, reproductive toxicants, or irritants as demonstrated by the manufacturer through appropriate testing.
• Minimal chemical emissions: Products that have minimal emissions of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs). Products that also maximize resource and energy efficiency while reducing chemical emissions.
• Low-VOC assembly: Materials installed with minimal VOC-producing compounds, or no-VOC mechanical attachment methods and minimal hazards.
• Moisture resistant: Products and systems that resist moisture or inhibit the growth of biological contaminants in buildings.
• Healthfully maintained: Materials, components, and systems that require only simple, non-toxic, or low-VOC methods of cleaning.
• Systems or equipment: Products that promote healthy IAQ by identifying indoor air pollutants or enhancing the air quality.
3. Energy Efficiency
Energy Efficiency can be maximized by utilizing materials and systems that meet the following criteria:
• Materials, components, and systems that help reduce energy consumption in buildings and facilities.
4. Water Conservation
Water Conservation can be obtained by utilizing materials and systems that meet the following criteria:
• Products and systems that help reduce water consumption in buildings and conserve water in landscaped areas.
5. Affordability
Affordability can be considered when building product life-cycle costs are comparable to conventional materials or as a whole, are within a project-defined percentage of the overall budget.
Benefits of Green Building
Buildings have an enormous impact on the environment, human health, and the economy. The successful adoption of green building strategies can maximize both the economic and environmental performance of buildings.
1. Environmental benefits
2.Economic benefits
3.Social benefits
1. Environmental benefits
▪ Enhance and protect biodiversity and ecosystems
▪ Improve air and water quality
▪ Reduce waste streams
▪ Conserve and restore natural resources
2. Economic benefits
▪ Reduce operating costs
▪ Create, expand, and shape markets for green product and services
▪ Improve occupant productivity
▪ Optimize life-cycle economic performance
3. Social benefits
▪ Enhance occupant comfort and health
▪ Heighten aesthetic qualities
▪ Minimize strain on local infrastructure
▪ Improve overall quality of life